What is the difference between ML, DL, AI, and Data Science?
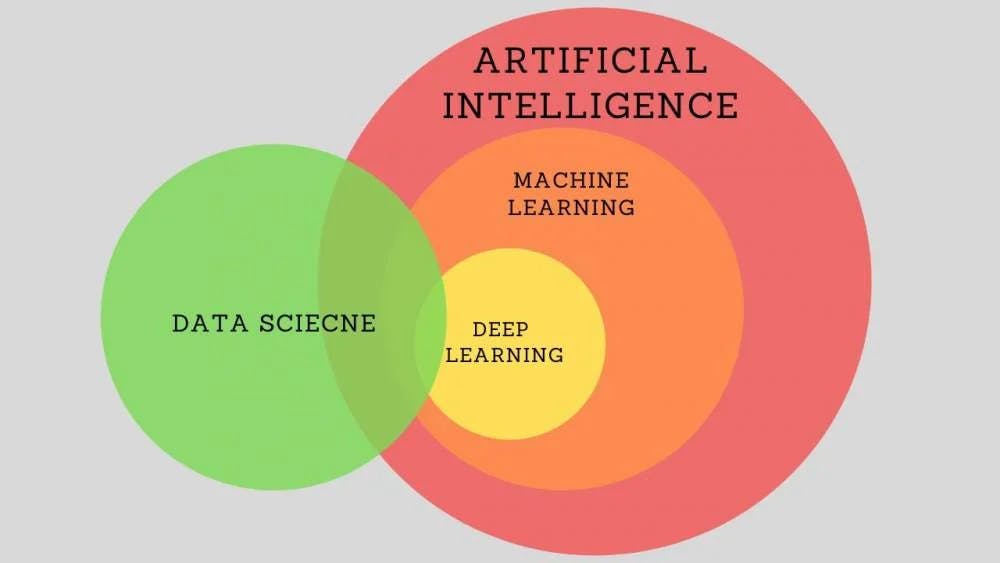
Machine Learning:
ML is a form of AI that is based on more data and it can change actions and responses, which will make it more efficient, adaptable and scalable. e.g., navigation apps and recommendation engines.
Machine Learning Classified into:-
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
- Reinforcement Learning
Data Science:
Data science has many tools, techniques, and algorithms called from these fields, plus others –to handle big data.
The goal of data science, somewhat similar to machine learning, is to make accurate predictions and to automate and perform transactions in real-time, such as purchasing internet traffic or automatically generating content.
Data science relies less on math and coding and more on data and building new systems to process the data.
Relying on the fields of data integration, distributed architecture, automated machine learning, data visualization, data engineering, and automated data-driven decisions, data science can cover an entire spectrum of data processing, not only the algorithms or statistics related to data.
Deep Learning:
It is a technique for implementing ML.
ML provides the desired output from a given input, but DL reads the input and applies it to other data. In ML, we can easily classify the flower based on its features. Suppose you want a machine to look at an image and determine what it represents to the human eye, whether a face, flower, landscape, truck, building, etc.
Machine learning is not sufficient for this task because machine learning can only produce an output from a data set – whether according to a known algorithm or based on the inherent structure of the data. You might be able to use machine learning to determine whether an image was of an “X” – a flower, say – and it would learn and get more accurate. But that output is binary (yes/no) and is dependent on the algorithm, not the data. In the image recognition case, the outcome is not binary and not dependent on the algorithm.
The neural network performs MICRO calculations with computational on many layers. Neural networks also support weighting data for ‘confidence. These results in a probabilistic system, vs. deterministic, and can handle tasks that we think of as requiring more ‘human-like’ judgment.
Artificial Intelligence:
AI is pure math and science, but when it became computational, it started to solve human problems formalized into a subset of computer science.
Artificial intelligence has changed the original computational statistics paradigm to the modern idea that machines could mimic actual human capabilities, such as decision-making and performing more “human” tasks.
Modern AI into two categories:
General AI - Planning, decision making, identifying objects, recognizing sounds, social & business transactions.
Applied AI - driverless/ Autonomous car or machine smartly trade stocks.
